Java基礎(chǔ)之List內(nèi)元素的排序性能對(duì)比
在日常開(kāi)發(fā)中,獲取一批數(shù)據(jù)后,可能需要跟據(jù)一定規(guī)則對(duì)這批數(shù)據(jù)進(jìn)行排序操作。在JAVA中,動(dòng)態(tài)數(shù)組ArrayList經(jīng)常被用來(lái)存儲(chǔ)數(shù)據(jù),因此如何高效對(duì)ArrayList中元素進(jìn)行排序,形成符合條件的數(shù)據(jù)集是日常開(kāi)發(fā)必須要考慮的問(wèn)題。本文將分析常用ArrayList排序的幾種方式,包括集合框架提供的Collections.sort方法、實(shí)現(xiàn)Comparable接口、以及JAVA 8 stream流中提供的排序方法,同時(shí)對(duì)比同一條件不同數(shù)據(jù)集大小的排序性能。
二、按條件排序幾種方案及性能對(duì)比2.1 利用集合框架提供的Collections.sort實(shí)現(xiàn)排序private ArrayList<StreamConfig> testCollectionSort(ArrayList<StreamConfig> lists) {Collections.sort(lists, new Comparator<StreamConfig>() { @Override public int compare(StreamConfig s1, StreamConfig s2) {return s2.getLostThreshold() - s1.getLostThreshold(); }});return lists; }
@Data@ToStringpublic class StreamConfig { /** * 主鍵 */ private Long id; /** * 分片檢測(cè)(檢測(cè)閾值) */ private Integer detectRate; /** * 上報(bào)閾值 */ private Integer lostThreshold; /** * 上報(bào)周期(單位:秒) */ private Integer reportRate; /** * 創(chuàng)建時(shí)間 */ private Date createTime; /** * 修改時(shí)間 */ private Date modifyTime;}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); log.info('Collection.sort 排序開(kāi)始時(shí)間為:{}', System.currentTimeMillis()); ArrayList<StreamConfig> list = testCollectionSort(lists); long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); log.info('Collection.sort 耗費(fèi)總時(shí)間為:{} ms', endTime - startTime);2.2 實(shí)現(xiàn)Comparable接口
@Data@ToStringpublic class StreamConfig implements Comparable<StreamConfig>{ /** * 主鍵 */ private Long id; /** * 分片檢測(cè)(檢測(cè)閾值) */ private Integer detectRate; /** * 上報(bào)閾值(丟失率大于多少不再上報(bào)) */ private Integer lostThreshold; /** * 上報(bào)周期(單位:秒) */ private Integer reportRate; /** * 創(chuàng)建時(shí)間 */ private Date createTime; /** * 修改時(shí)間 */ private Date modifyTime; /** * 備注 */ private String remark; /** * nodeCode */ private String nodeCode; /** * 流媒體Id */ private String unitId; @Override public int compareTo(StreamConfig o) {return this.getLostThreshold() - o.getLostThreshold(); }}
long comparableStartTime = System.currentTimeMillis();Collections.sort(list3);long comparableEndTime = System.currentTimeMillis();log.info('Comparable 耗費(fèi)總時(shí)間為:{}', comparableEndTime - comparableStartTime);2.3 利用JAVA 8 stream流實(shí)現(xiàn)排序
long streamStartTime = System.currentTimeMillis();log.info('java 8 stream流式處理開(kāi)啟:{}', streamStartTime);List<StreamConfig> collect = list2.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(StreamConfig::getLostThreshold)).collect(Collectors.toList());log.info('java 8 stream流式所花時(shí)間為:{} ms', System.currentTimeMillis() - streamStartTime);2.4 性能對(duì)比
測(cè)試方案:
為了防止Collection.sort與實(shí)現(xiàn)Comparable接口兩種方法的相互干擾,將實(shí)現(xiàn)Comparable的方案單獨(dú)測(cè)試,數(shù)據(jù)量集分別為1000、10000、100000,結(jié)果單位為毫秒(ms),每個(gè)數(shù)據(jù)集測(cè)試五次,取平均值。
測(cè)試代碼如下:
public String test() {ArrayList<StreamConfig> lists = new ArrayList<>(100000);for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) { StreamConfig streamConfig = new StreamConfig(); streamConfig.setReportRate((int) (Math.random() * 10000)); streamConfig.setLostThreshold((int) (Math.random() * 100000)); streamConfig.setDetectRate((int) (Math.random() * 10000)); streamConfig.setCreateTime(randomDate('2019-01-01', '2021-05-31')); streamConfig.setId(System.currentTimeMillis() + (int) (Math.random() * 100000)); lists.add(streamConfig);}ArrayList<StreamConfig> list2 = new ArrayList<>(lists);ArrayList<StreamConfig> list3 = new ArrayList<>(lists);long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();log.info('Collection.sort 排序開(kāi)始時(shí)間為:{}', System.currentTimeMillis());ArrayList<StreamConfig> list = testCollectionSort(lists);long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();log.info('Collection.sort 耗費(fèi)總時(shí)間為:{} ms', endTime - startTime);log.info('Comparable 排序開(kāi)始時(shí)間為:{}', System.currentTimeMillis());long comparableStartTime = System.currentTimeMillis();Collections.sort(list3);long comparableEndTime = System.currentTimeMillis();log.info('Comparable 耗費(fèi)總時(shí)間為:{}', comparableEndTime - comparableStartTime);long streamStartTime = System.currentTimeMillis();log.info('java 8 stream流式處理開(kāi)啟:{}', streamStartTime);List<StreamConfig> collect = list2.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(StreamConfig::getLostThreshold).reversed()).collect(Collectors.toList());log.info('java 8 stream流式處理結(jié)束:{}', System.currentTimeMillis());log.info('java 8 stream流式所花時(shí)間為:{} ms', System.currentTimeMillis() - streamStartTime);return 'success'; }
測(cè)試結(jié)果如下:
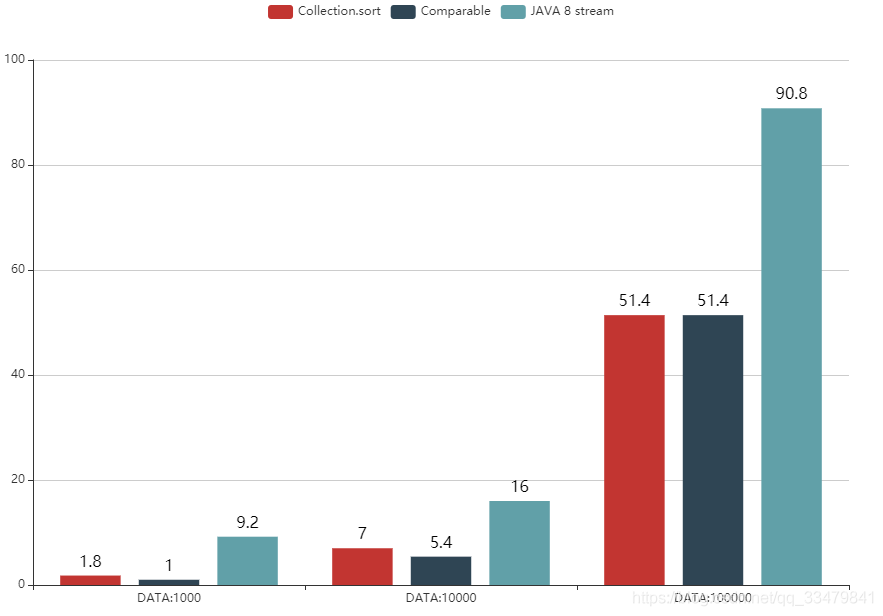
1.由測(cè)試結(jié)果來(lái)看,在數(shù)據(jù)量分別是1000、10000、100000的數(shù)據(jù)集下,java 8 stream的排序方案所花費(fèi)時(shí)間遠(yuǎn)大于Collection.sort方案和實(shí)現(xiàn)Comparable接口方案;
2.由測(cè)試結(jié)果來(lái)看,Collection.sort方案和實(shí)現(xiàn)Comparable接口方案在數(shù)據(jù)量越大所花費(fèi)的時(shí)間越接近,這兩種方案在數(shù)據(jù)量相同時(shí)的差異也不是很大;
3.本文所對(duì)比的是單條件下(也就是跟據(jù)lostThreshold屬性值進(jìn)行對(duì)比),多條件可能會(huì)略有差異,后續(xù)可針對(duì)多條件進(jìn)行一些數(shù)據(jù)測(cè)試與驗(yàn)證;
4.由測(cè)試結(jié)果可以得出,單條件對(duì)比時(shí),Collection.sort方案和實(shí)現(xiàn)Comparable接口方案具有更高性能,建議數(shù)據(jù)量較大時(shí)盡量采用這兩種排序方式。
到此這篇關(guān)于Java基礎(chǔ)之List元素的排序性能的文章就介紹到這了,更多相關(guān)Java List元素的排序性能內(nèi)容請(qǐng)搜索好吧啦網(wǎng)以前的文章或繼續(xù)瀏覽下面的相關(guān)文章希望大家以后多多支持好吧啦網(wǎng)!
相關(guān)文章:
1. el-input無(wú)法輸入的問(wèn)題和表單驗(yàn)證失敗問(wèn)題解決2. 不要在HTML中濫用div3. react腳手架配置代理的實(shí)現(xiàn)4. JavaScript中顏色模型的基礎(chǔ)知識(shí)與應(yīng)用詳解5. XML入門(mén)的常見(jiàn)問(wèn)題(三)6. JavaScript快速實(shí)現(xiàn)一個(gè)顏色選擇器7. CSS3實(shí)例分享之多重背景的實(shí)現(xiàn)(Multiple backgrounds)8. 前端html+css實(shí)現(xiàn)動(dòng)態(tài)生日快樂(lè)代碼9. Jquery使用原生AJAX方法請(qǐng)求數(shù)據(jù)10. React實(shí)現(xiàn)一個(gè)倒計(jì)時(shí)hook組件實(shí)戰(zhàn)示例
 網(wǎng)公網(wǎng)安備
網(wǎng)公網(wǎng)安備