Spring的BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口示例代碼詳解
BeanFactoryPostProcessor 接口是 Spring 初始化 BeanFactory 時對外暴露的擴(kuò)展點(diǎn),Spring IoC 容器允許 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 在容器實(shí)例化任何 bean 之前讀取 bean 的定義,并可以修改它。
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 繼承自 BeanFactoryPostProcessor,比 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 具有更高的優(yōu)先級,主要用來在常規(guī)的 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 檢測開始之前注冊其他 bean 定義。特別是,你可以通過 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 來注冊一些常規(guī)的 BeanFactoryPostProcessor,因為此時所有常規(guī)的 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 都還沒開始被處理。
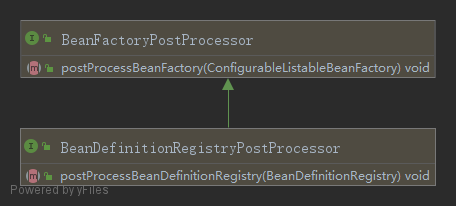
注意點(diǎn):通過BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 注冊的 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 接口的postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法將得不到調(diào)用,具體的原因會在下面的代碼中解釋。
BeanFactoryPostProcessor 接口調(diào)用機(jī)制BeanFactoryPostProcessor 接口的調(diào)用在 AbstractApplicationContext#invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors方法中。
protected void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory, getBeanFactoryPostProcessors());// Detect a LoadTimeWeaver and prepare for weaving, if found in the meantime// (e.g. through an @Bean method registered by ConfigurationClassPostProcessor)if (beanFactory.getTempClassLoader() == null && beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) {beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory));beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));}}
進(jìn)入PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory, getBeanFactoryPostProcessors())方法:
public static void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> beanFactoryPostProcessors) { // 用于存放已經(jīng)處理過的Bean名字Set<String> processedBeans = new HashSet<>(); // 一般會進(jìn)入這個判斷if (beanFactory instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistry) {BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = (BeanDefinitionRegistry) beanFactory; // 所謂的regularPostProcessors就是指實(shí)現(xiàn)BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的BeanList<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> regularPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(); // 所謂的registryProcessors就是指實(shí)現(xiàn)BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口的BeanList<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> registryProcessors = new ArrayList<>(); // 這邊遍歷的是通過ApplicationContext接口注冊的BeanFactoryPostProcessor和BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口 // 需要和BeanFactory中BeanDefinitionMap中的BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口區(qū)分開for (BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor : beanFactoryPostProcessors) {if (postProcessor instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) {BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor registryProcessor =(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) postProcessor; //如果是BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor,則先進(jìn)行postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry處理,這個方法一般進(jìn)行BeanDefinition注冊,從這邊可以看出BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口的方法先調(diào)用,所以優(yōu)先級高于BeanFactoryPostProcessor // 通過這個代碼可以看出,通過ApplicationContext直接注冊的BeanFactoryPostProcessor和BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor并不支持Order接口,而是根據(jù)注冊的順序執(zhí)行registryProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry); // 保存這個BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor,因為還要執(zhí)行這個類的BeanFactoryPostProcessor方法;registryProcessors.add(registryProcessor);}else { // 保存,后面還要執(zhí)行這個類的BeanFactoryPostProcessor方法;regularPostProcessors.add(postProcessor);}}List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> currentRegistryProcessors = new ArrayList<>(); // 這邊獲取的是BeanFactory中的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessorString[] postProcessorNames =beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) { //先處理PriorityOrdered標(biāo)注的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessorif (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class)); //將其標(biāo)記為已經(jīng)處理,防止重復(fù)處理processedBeans.add(ppName);}} // 將其排序,以便按順序處理sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory); // 將其保存,以便處理這個類的BeanFactoryPostProcessor方法registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors); // 執(zhí)行BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口方法invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry); // 清除,以便開始處理@Order標(biāo)注的注解currentRegistryProcessors.clear(); // 注意:這邊重新獲取BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor是有深意的,因為上面在處理@PriorityOrdered標(biāo)注的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor時可能又注入了新的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor。postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) { // 判斷是否處理過,防止重復(fù)處理,下面的邏輯和上面相同, 不介紹了if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName) && beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));processedBeans.add(ppName);}}sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);currentRegistryProcessors.clear(); // 處理不標(biāo)注注解的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessorboolean reiterate = true;while (reiterate) {reiterate = false;postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));processedBeans.add(ppName);reiterate = true;}}sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);currentRegistryProcessors.clear();}// 調(diào)用postProcessBeanFactory 方法,所以BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor中的postProcessBeanFactory方法的優(yōu)先級要高。invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(registryProcessors, beanFactory);invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(regularPostProcessors, beanFactory);}else {// Invoke factory processors registered with the context instance.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactoryPostProcessors, beanFactory);}// 開始處理BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口String[] postProcessorNames =beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class, true, false);// 也是按照@PriorityOrdered @Ordered 和普通的方式進(jìn)行處理List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) { // 可能已經(jīng)處理過if (processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {// skip - already processed in first phase above}else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));}else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);}else {nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);}} // 先執(zhí)行@PriorityOrdered標(biāo)注的接口sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); // 處理@Order標(biāo)注的類List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(orderedPostProcessorNames.size());for (String postProcessorName : orderedPostProcessorNames) { // 這邊通過名字重新拿了Bean,應(yīng)該是怕上面的處理改變了BeanorderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));}sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);// 最后調(diào)用普通的BeanFactoryPostProcessorList<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.size());for (String postProcessorName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) {nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));}invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(nonOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);// Clear cached merged bean definitions since the post-processors might have// modified the original metadata, e.g. replacing placeholders in values...beanFactory.clearMetadataCache();}簡單總結(jié)
上面的方法看起來很長很復(fù)雜,但其實(shí)干的事情并不多,就調(diào)用了BeanFactoryPostProcessor和BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口的實(shí)現(xiàn)。這邊再簡單總結(jié)下具體的過程:
step1:執(zhí)行通過ApplicationContext#addBeanFactoryPostProcessor()方法注冊的BeanFactoryPostProcessor和BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor。
具體過程如下:假如通過ApplicationContext注冊了一個BeanFactoryPostProcessor和BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor,那么會先執(zhí)行BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法,但是BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的postProcessBeanFactory方法和BeanFactoryPostProcessor的postProcessBeanFactory方法暫時都不會在這步執(zhí)行。
另外需要注意的是:通過ApplicationContext注冊的BeanFactoryPostProcessor和BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor都不支持@PriorityOrdered和@Ordered順序處理,而是按照我們添加的順序處理
step2:處理BeanFactory中的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor,處理的順序是先處理@PriorityOrdered標(biāo)注的,再處理@Ordered標(biāo)注的,最后處理普通的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor。到這邊,所有BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口的postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法都已經(jīng)調(diào)用完畢,下面就開始處理BeanFactoryPostProcessor的postProcessBeanFactory方法。
step3:調(diào)用BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor實(shí)現(xiàn)的postProcessBeanFactory方法(因為BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor是BeanFactoryPostProcessor的子接口)
step4:調(diào)用通過ApplicationContext#addBeanFactoryPostProcessor()注冊的“單純”的BeanFactoryPostProcessor
step5:調(diào)用BeanFactory中的BeanFactoryPostProcessor,調(diào)用順序也是按照@PriorityOrdered和@Ordered順序處理,沒有這兩個注解的最后處理。
好了,到這邊BeanFactoryPostProcessor和BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口就已經(jīng)處理完了。后面我們會拿ConfigurationClassPostProcessor 這個特殊的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor做列子講下具體流程,這邊只是介紹BeanFactoryPostProcessor的調(diào)用機(jī)制。
到此這篇關(guān)于Spring的BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的文章就介紹到這了,更多相關(guān)Spring BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口內(nèi)容請搜索好吧啦網(wǎng)以前的文章或繼續(xù)瀏覽下面的相關(guān)文章希望大家以后多多支持好吧啦網(wǎng)!
相關(guān)文章:
1. Python如何批量生成和調(diào)用變量2. ASP.Net Core對USB攝像頭進(jìn)行截圖3. ASP.NET MVC實(shí)現(xiàn)橫向展示購物車4. Python 中如何使用 virtualenv 管理虛擬環(huán)境5. Python獲取B站粉絲數(shù)的示例代碼6. Python基于requests實(shí)現(xiàn)模擬上傳文件7. python利用opencv實(shí)現(xiàn)顏色檢測8. windows服務(wù)器使用IIS時thinkphp搜索中文無效問題9. ASP.Net Core(C#)創(chuàng)建Web站點(diǎn)的實(shí)現(xiàn)10. 通過CSS數(shù)學(xué)函數(shù)實(shí)現(xiàn)動畫特效
 網(wǎng)公網(wǎng)安備
網(wǎng)公網(wǎng)安備